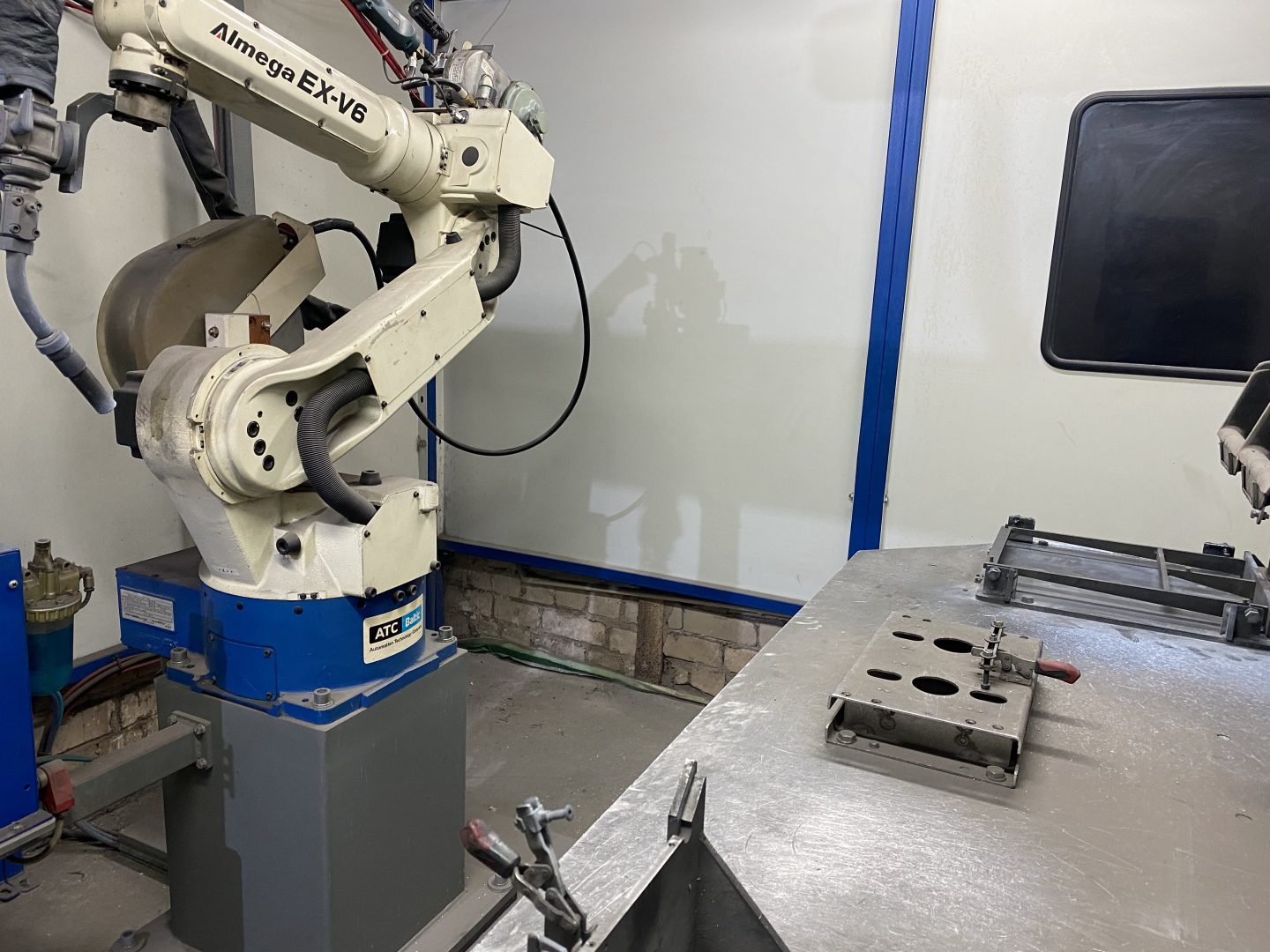
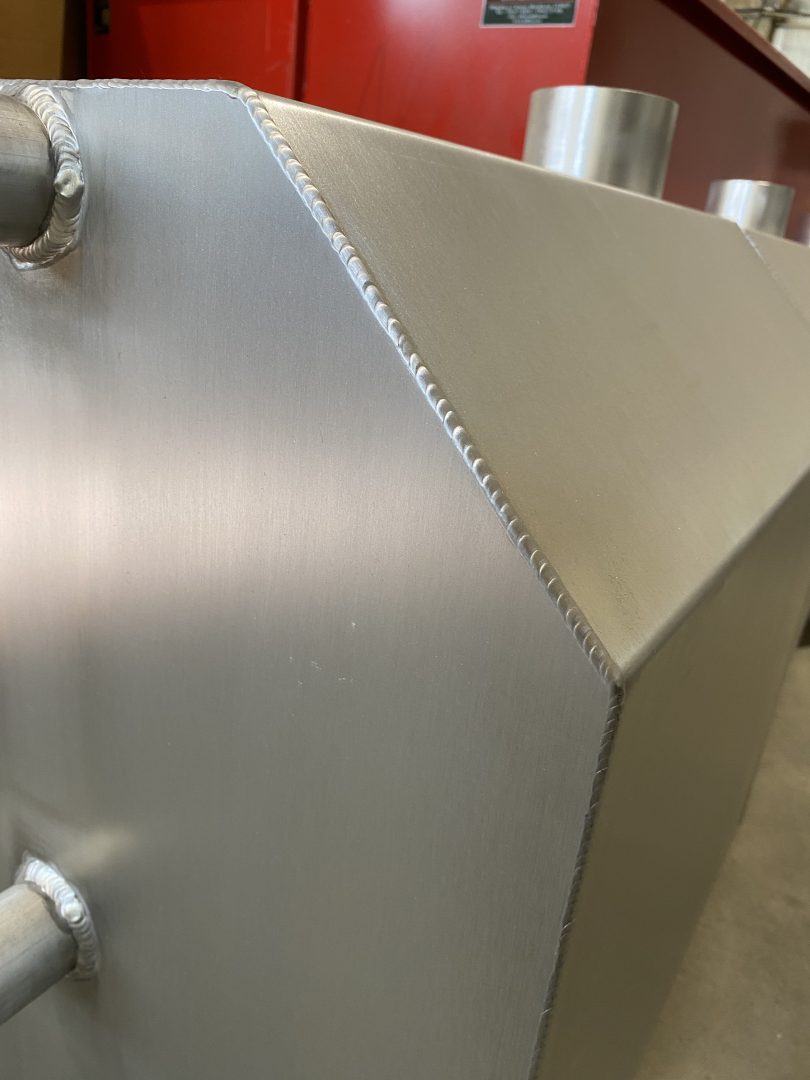
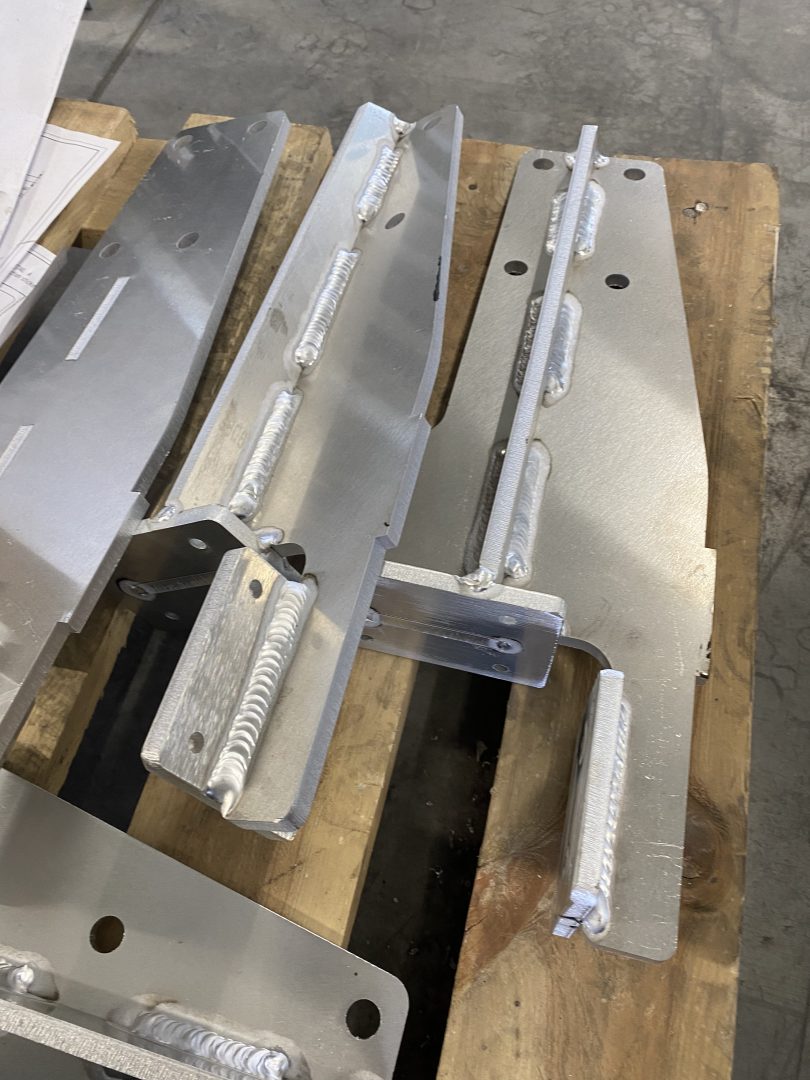
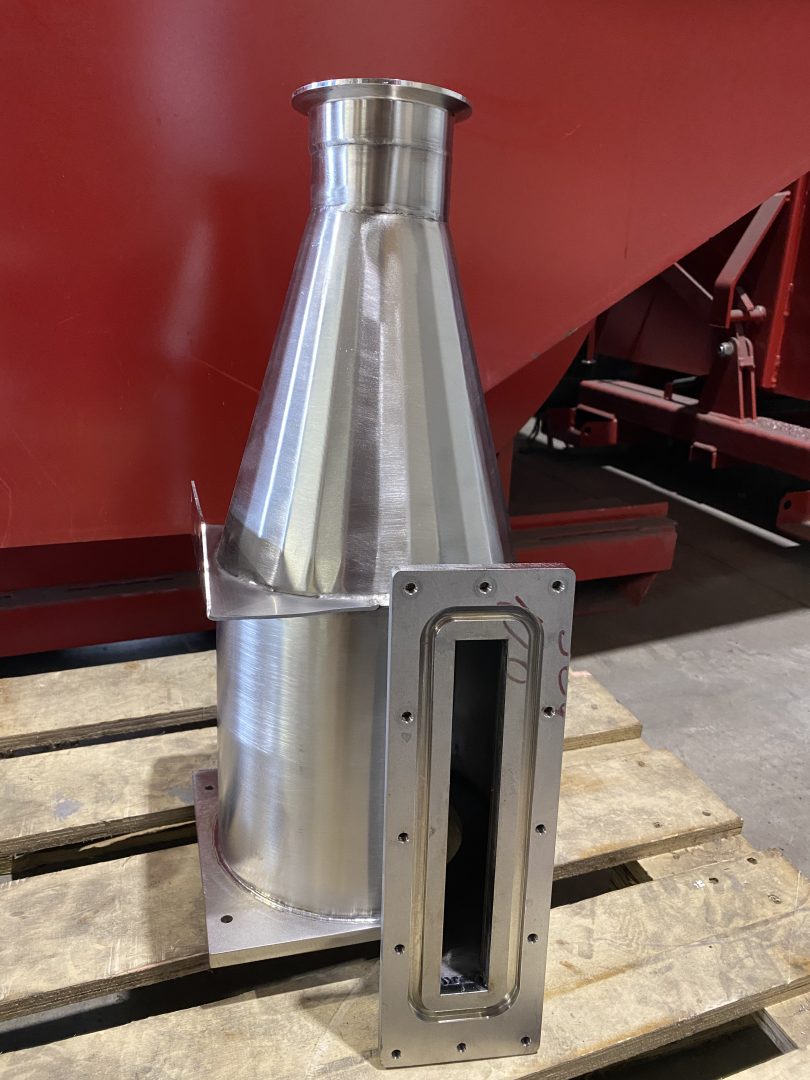
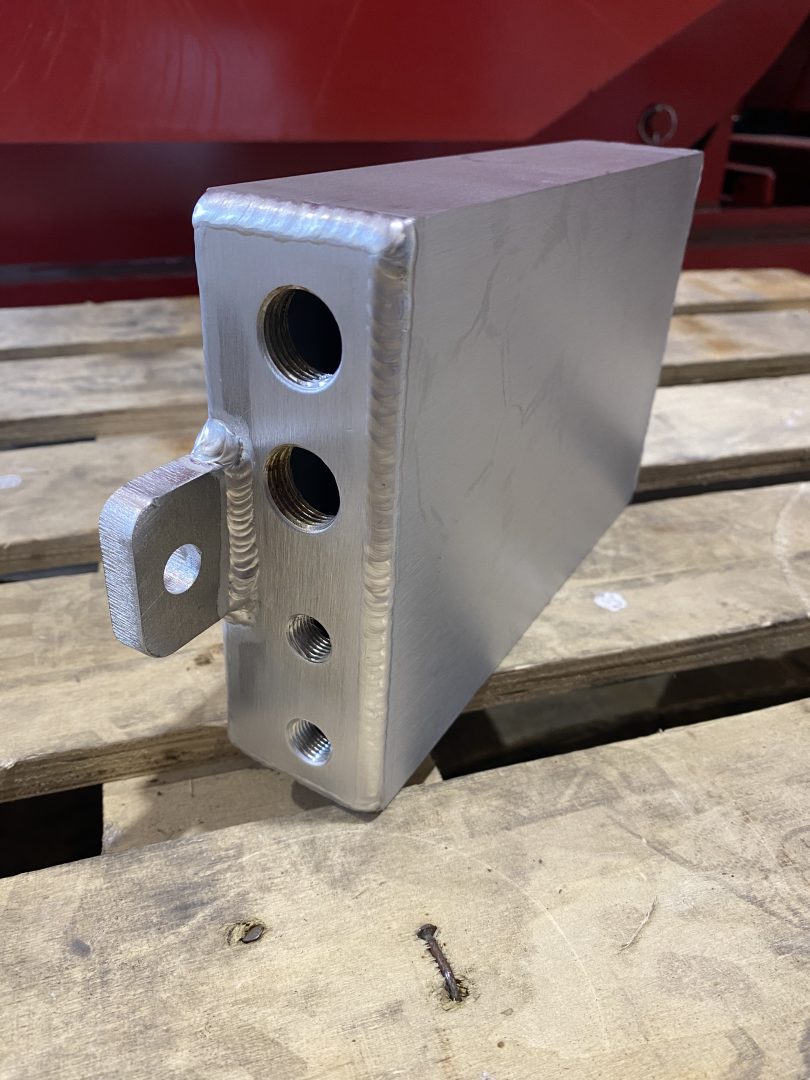
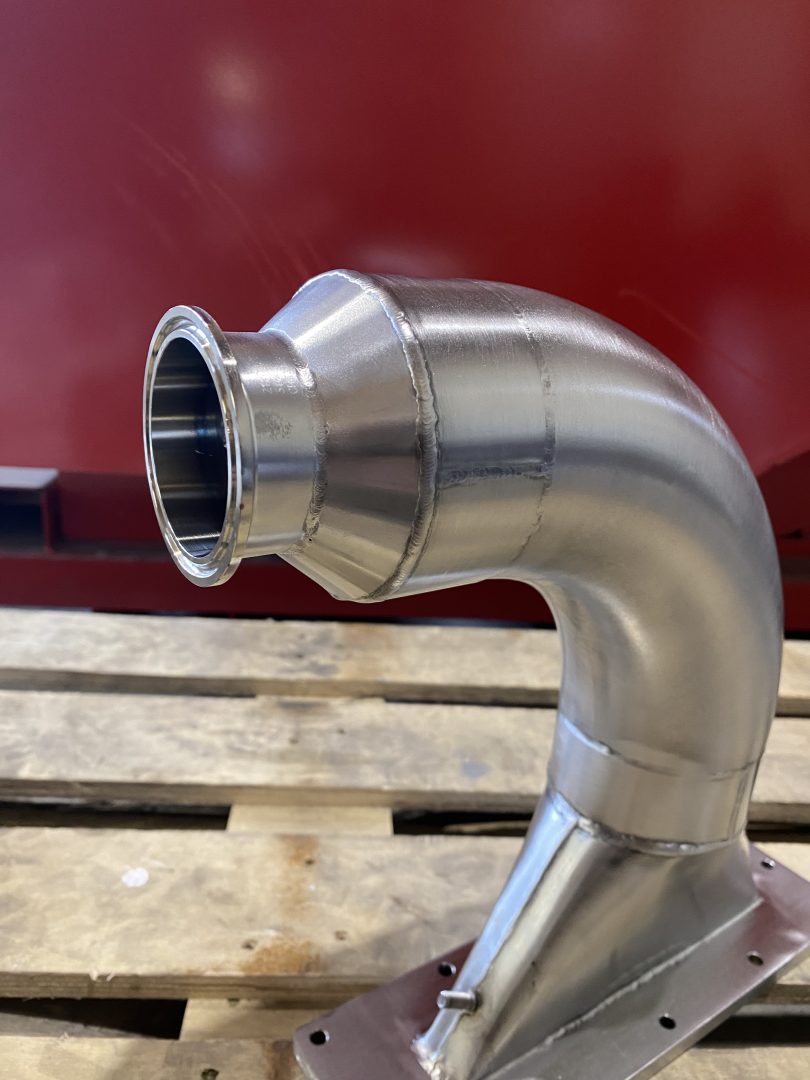
Welding is one of the most efficient methods for joining one metal to another. It is also the only way to connect separate metal parts so that they can function as a single unit.
Welding, as a method of joining structures or components, has been used for centuries, and modern industries, construction, and all manufacturing sectors cannot function without welding work.
Welding can be used to create structures from various metals and their alloys, as well as to produce structures from parts obtained through other processing methods, such as stamping, rolling, forging, casting, etc. The question often arises - why choose welding and what are its advantages? Compared to other methods of metal structure production, welded structures are generally lighter.
In addition, welding can save from 10 to 50 percent of metal. It is important to note that some structures can only be made through welding, or certain new materials can only be used through welding technology, and no other metal joining methods are suitable or as reliable. There are various welding methods. Currently, about 100 welding methods are used in different industrial sectors.
They all differ in some way, but they all have one common feature: two compacted metal pieces are welded together, with the surface at the welding location being heated, melted, or heated and filled with molten metal. In welding a metal structure, the edges of the components at the junction point melt. This is what distinguishes welding from soldering, where the edges of the components do not melt, making welding undoubtedly a superior method of joining metal structures than soldering.
The most common method of welding metal structures is fusion welding, during which the surfaces of the metal parts are heated by electric current, and more commonly, by gases. Welding is carried out using a filler material or electrode. When welding, they melt at a high temperature, fill the junction with the surface of the part, and solidify into a seam. When welding metals in this way, we use a mixture of acetylene and oxygen as a heat source.
Thin sheet steel, small and medium-diameter pipes, as well as copper, brass, aluminum, and their alloys are welded with gases. The advantage of acetylene gas is the low heat of welding, which is easy to control. Welding with acetylene gas has good filling properties for the seam, meaning they are strong, so we often recommend it to our customers. The seam needs to be slightly prepared or often not prepared at all.
This problem-free welding method is particularly useful when welding under complex conditions. For example, when building gas pipelines, where other welding methods are usually unsuitable or uneconomical, the oxygen-acetylene flame is a reliable auxiliary tool for a welder.
However, in Western Europe, the United States, and Japan, the most common practices currently are MIG/MAG welding methods. MIG is a welding method that uses inert gases as a protective shield, while MAG uses active gases. Both of these methods are popular due to their high productivity level and the possibility of easy mechanization. In MIG/MAG welding, filler metals are used, such as continuous welding wire or flux-cored wire.
Various metals are continuously melted by an electric arc generated by an electrical energy source. The electric arc and the molten metal are protected by shielding gases. In this case, inert means that the gases do not react with the molten metal or the electrode.
The inert gases used are argon and helium. Active gases provide more opportunities to optimize the process and achieve higher quality of the final welded product. When welding many materials, such as non-alloyed steel, active gases are required to ensure the stability and reliability of the process. Mixtures of active gases can be argon with carbon dioxide and argon with oxygen.
The choice of method in each specific case is discussed individually with each customer, depending on the type and characteristics of the structures and their further use.